ISO 1461 vs. ASTM A123
One of my customers has asked me to galvanize his product according to ISO 1461. Is this specification different from ASTM A123? And, if so, what are the differences?
*Updated in 2022
Summary
International Standards Organization ISO 1461, Hot Dip Galvanized Coatings on Fabricated Iron and Steel Articles - Specifications and Test Methods, is a general galvanizing specification. Hot-dip galvanizing to A123 will typically lead to a final quality which meets or exceeds ISO 1461.
This article provides a basic overview of the similarities and differences between ISO 1461 and A123 as they relate to coating thickness, appearance, repairs, adhesion, inspection, and sampling. It is not intended to be used as an exhaustive guide on the differences in terms of inspection requirements or contractual obligations when substituting one specification for the other.
Scope of Specifications
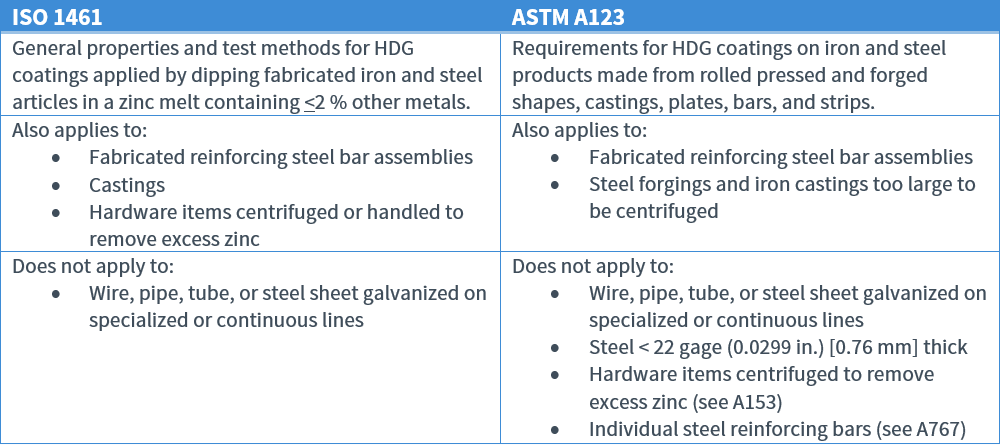
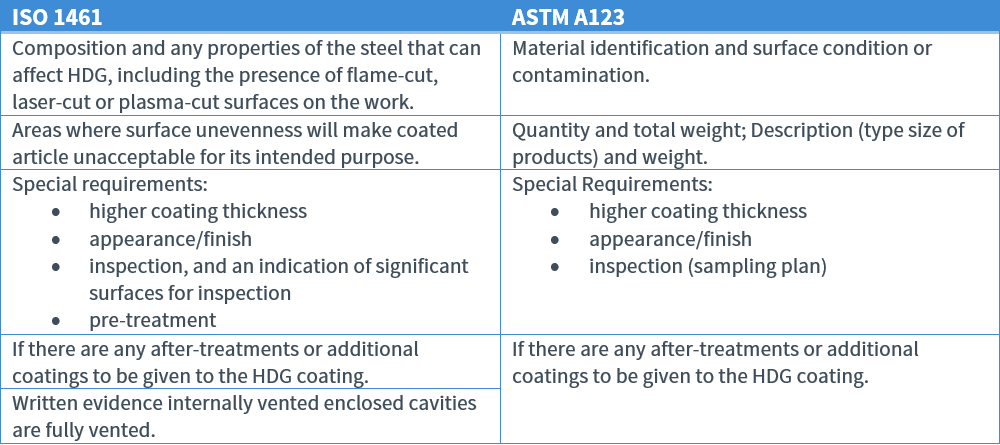
Ordering Information
The purchaser must provide the following:
Base Metal Considerations

Zinc and The Galvanizing Bath (Zinc Melt)
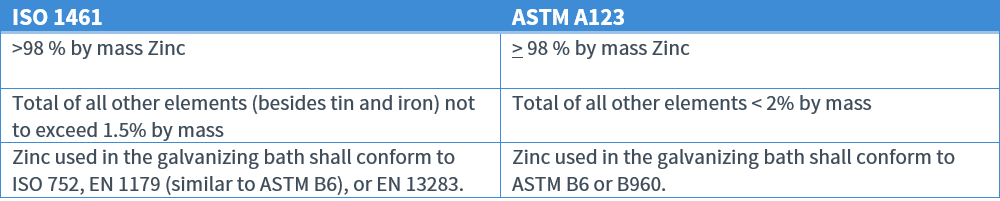
Coating Requirements
Coating Thickness for Articles That Are Not Centrifuged
The differences in minimum average coating thickness for most steel articles are small. In the specification, the ISO minimum coating thickness requirements are summed up into one table, which does not mention coating grades and does not require the user to reference two tables as with ASTM A123. Also, the ISO1461 specification lists minimum local coating thickness to which any one measurement must meet. These are 0.4-0.6 mils thinner than the minimum average coating thickness. In the ASTM specifications, only ASTM A153 has such minimum local thickness coating listed for castings and fasteners. Rolled, pressed and forged articles referred to ASTM A153 also have minimum local coating thickness; these articles are not specifically mentioned in the ISO specification.
A comparison of the standards finds they are very similar, with the ASTM Specs typically requiring more coating thickness on most types and thickness of steel.
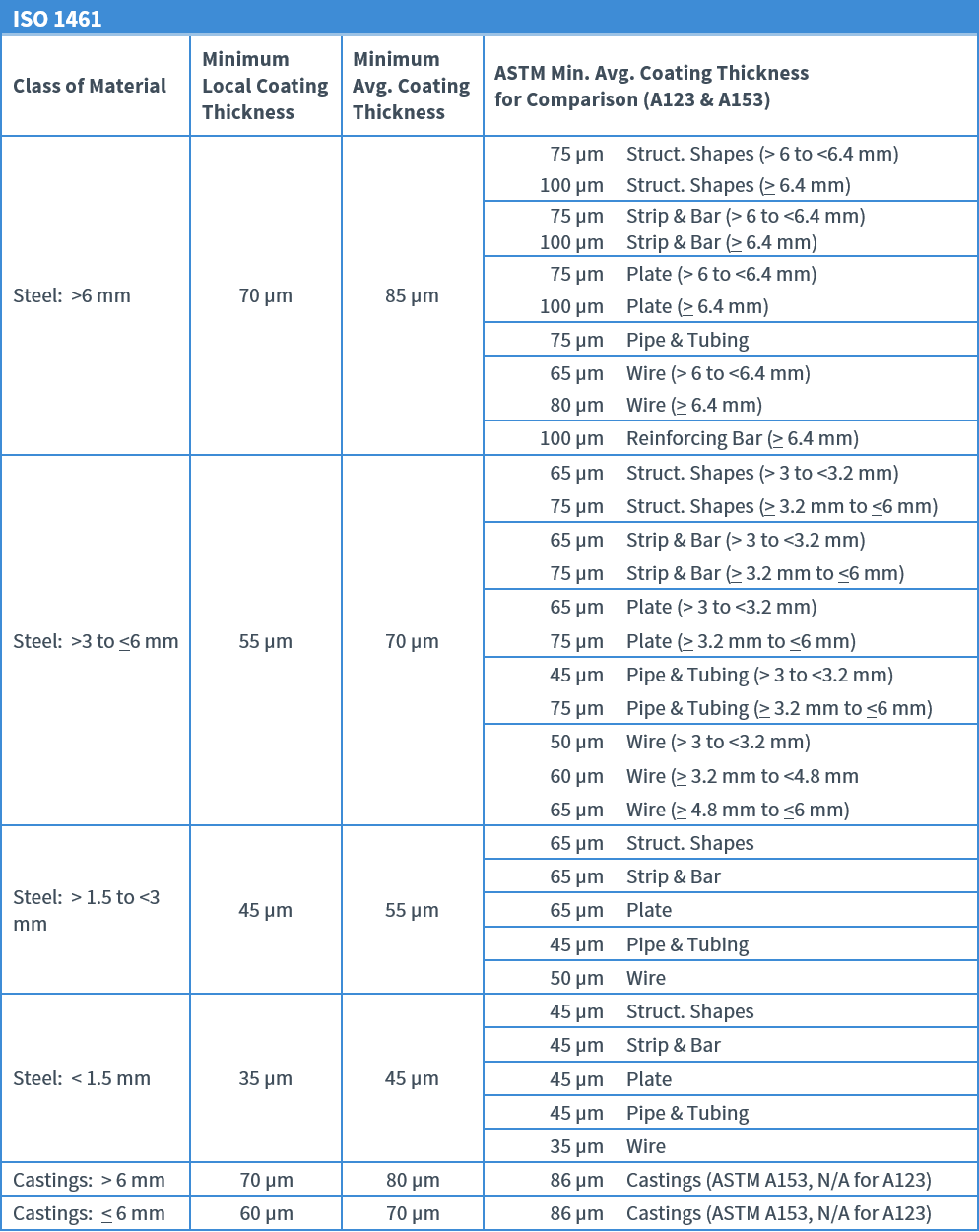
For further comparison, a summary of the ASTM A123 coating thickness requirements is provided below.
| Table 1: Minimum Average Coating Thickness Grade by Material Category | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Specimens Tested, Steel Thickness Range (Measured) in. [mm] | ||||||
| Material Category | <1/16 [<1.6] | >1/16 to <1/8 [>1.6 to <3.2] | >1/8 to 3/16 [>3.2 to < 4.8] | >3/16 to <1/4 [>4.8 to <6.4] | >1/4 to <5/8 [>6.4 to <16.0] | >5/8 [>16.0] |
| Structural Shapes | 45 | 65 | 75 | 75 | 100 | 100 |
| Strip and Bar | 45 | 65 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 100 |
| Plate | 45 | 65 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 100 |
| Pipe & Tubing | 45 | 45 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 |
| Wire | 35 | 50 | 60 | 65 | 80 | 80 |
| Reinforcing Bar | -- | -- | -- | -- | 100 | 100 |
| Forgings and Castings | -- | -- | -- | 100 | 100 | 100 |
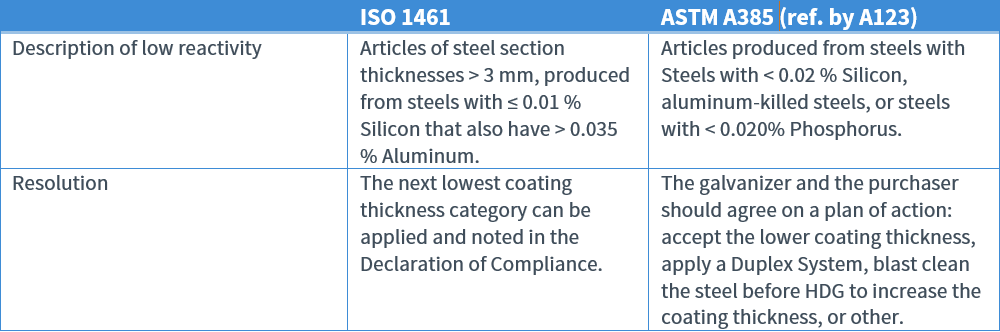
Resolving Concerns When Galvanizing Low Reactivity Steels
Steels with very low levels of silicon and aluminum-killed steels regularly present a challenge in developing a galvanized coating that meets the thickness requirements of the galvanizing specifications. To address these concerns, both galvanizing standards provide guidance to address occasional instances where normal coating thickness requirements cannot be achieved when galvanizing steels with low reactivity.
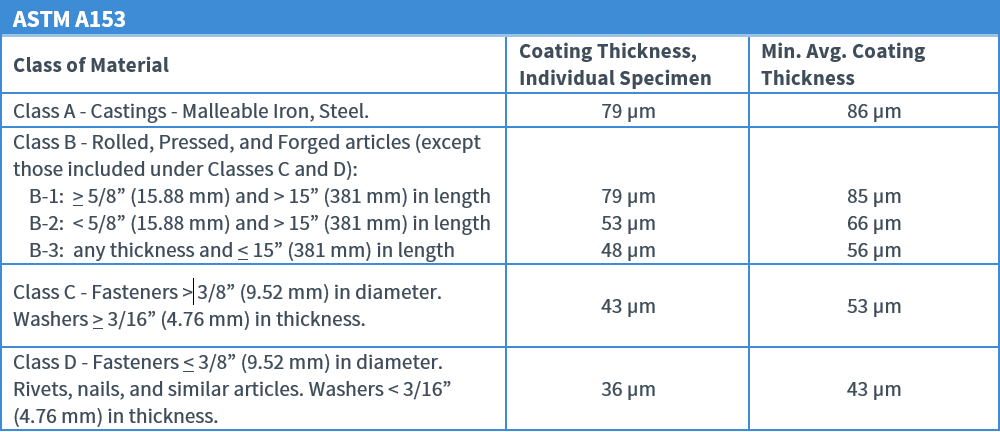
Coating Thickness for Centrifuged Articles
The ISO 1461 standard incorporates the ASTM equivalent of A153 regarding centrifuged articles into ISO 1461. It is more difficult to compare the ISO 1461 category requirements and ASTM A153 category requirements side by side for articles not centrifuged. This is because the ASTM material categories are defined through a combination of part size and steel thickness. A comparison of the tables is provided below:
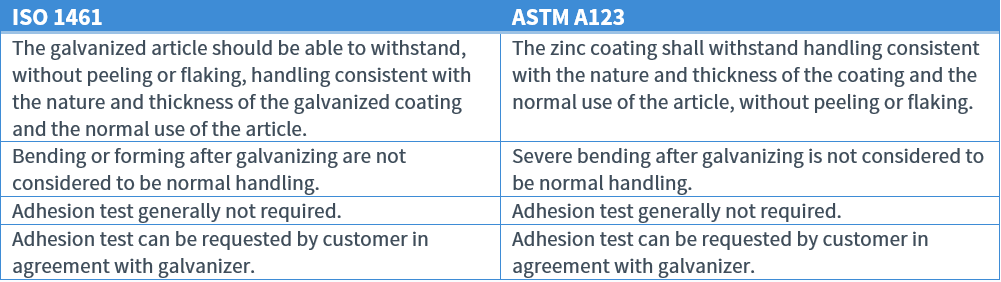
Adhesion/Adherence
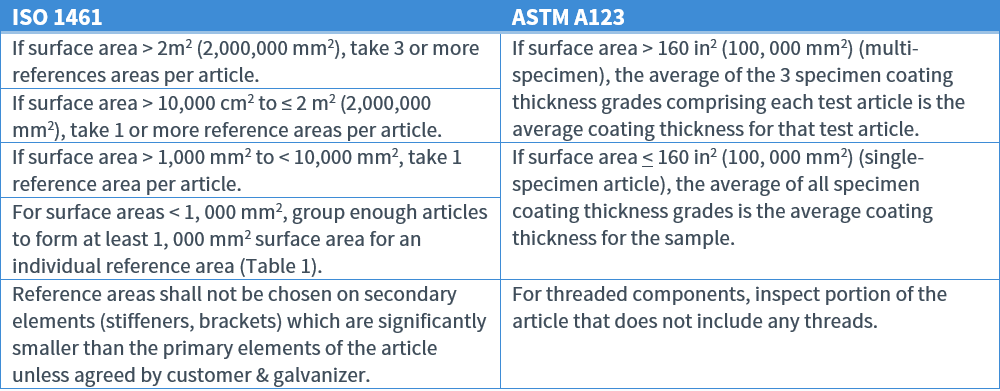
Sampling & Inspection
Inspection Lots

Control Sample Size vs. Lot Size

Reference Areas for Coating Thickness Inspection
For each reference area, five or more measurements are made at widely dispersed points to represent the entire surface area of the test specimen.
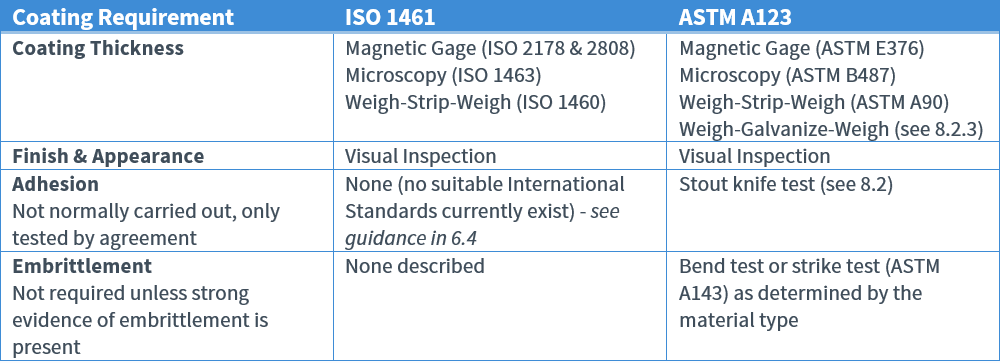
Test Methods
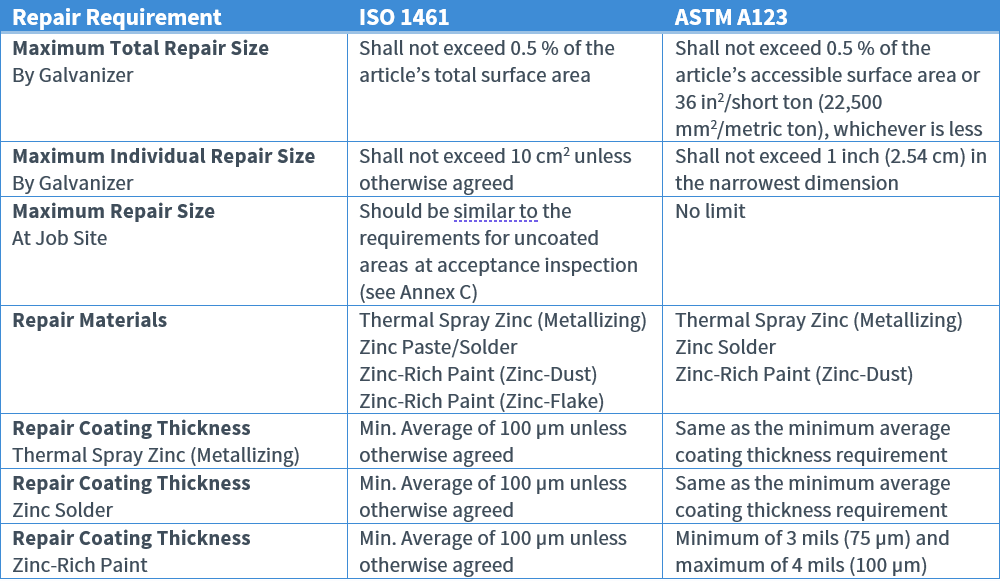
Repairs
Certificate/Declaration

© 2026 American Galvanizers Association. The material provided herein has been developed to provide accurate and authoritative information about after-fabrication hot-dip galvanized steel. This material provides general information only and is not intended as a substitute for competent professional examination and verification as to suitability and applicability. The information provided herein is not intended as a representation or warranty on the part of the AGA. Anyone making use of this information assumes all liability arising from such use.


