Coating Characteristics of Continuous Sheet Galvanizing
Note: Have questions about continuous hot-dip galvanizing? Contact the GalvInfo Center
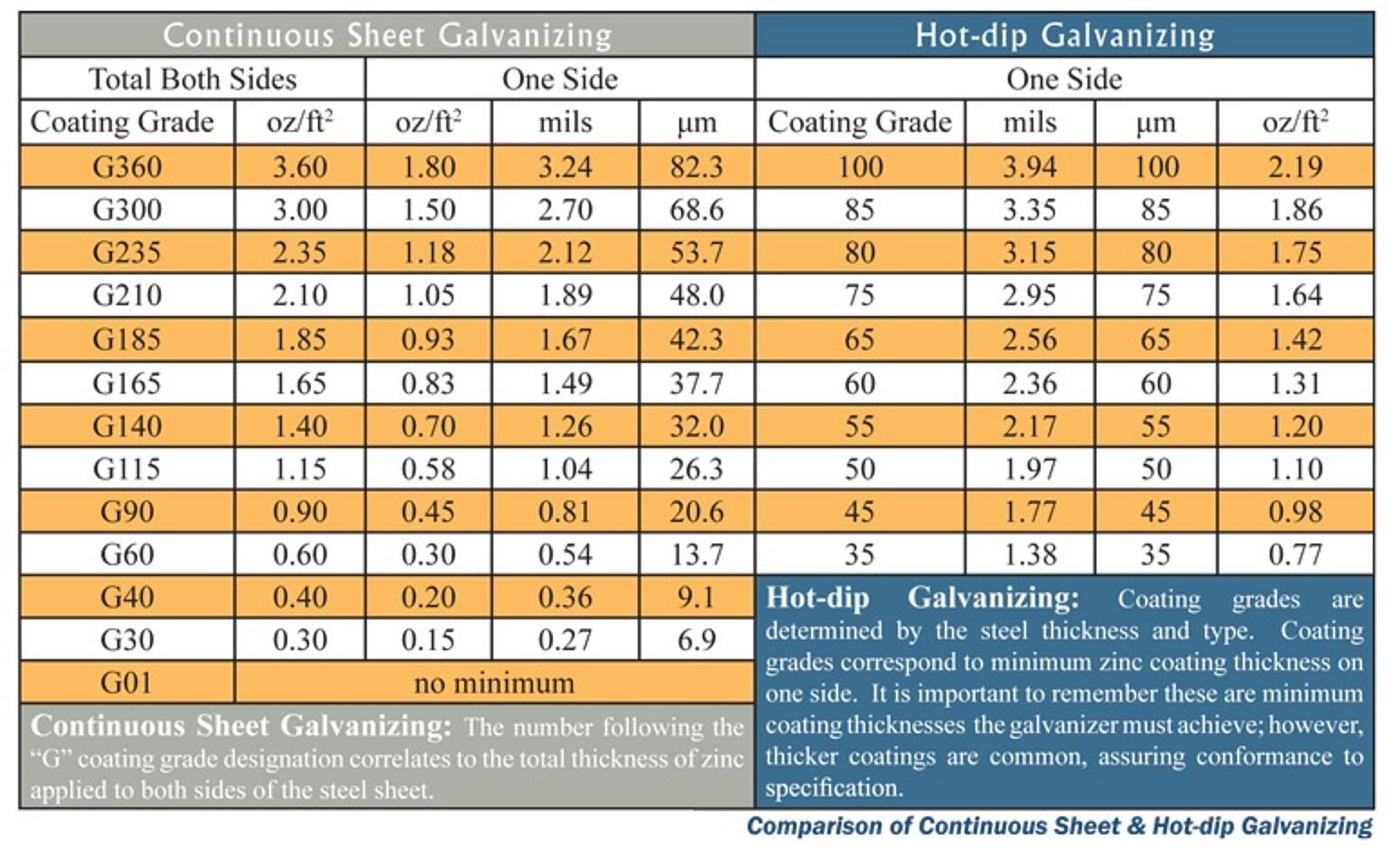
After galvanizing, the continuous zinc coating is physically wiped using air knives to produce a uniform coating across the width of the strip. The uniform coating consists almost entirely of unalloyed zinc and has sufficient ductility to withstand deep drawing or bending without damage. A variety of coating weights and types are available, ranging up to just over 3 mils (76 µm) per side. One of the most common zinc coatings is Class G90, which has 0.9 oz/ft2 of zinc (total both sides) or about 0.80 mils (20 µm) thickness per side. Continuous sheet galvanized coatings often get confused with batch hot-dip galvanized coatings because the term galvanizing is used interchangeably. The table below compares the available coating grades of continuous and batch hot-dip galvanizing and their corresponding coating thicknesses. Zinc coating thickness is proportional to the service life as evidenced in the Time to First Maintenance Chart. Continuously galvanized sheet steels are used to make cars, appliances, corrugated roofing and siding, and culvert pipe. The coated product can be suitably treated for painting, which will increase the service life. Because of the thin coating, this product normally is used for interior applications or where exposure to corrosive elements is mild.
See Also: Zinc Coatings Publication
© 2026 American Galvanizers Association. The material provided herein has been developed to provide accurate and authoritative information about after-fabrication hot-dip galvanized steel. This material provides general information only and is not intended as a substitute for competent professional examination and verification as to suitability and applicability. The information provided herein is not intended as a representation or warranty on the part of the AGA. Anyone making use of this information assumes all liability arising from such use.

