Atmospheric corrosion of hot-dip galvanized steel
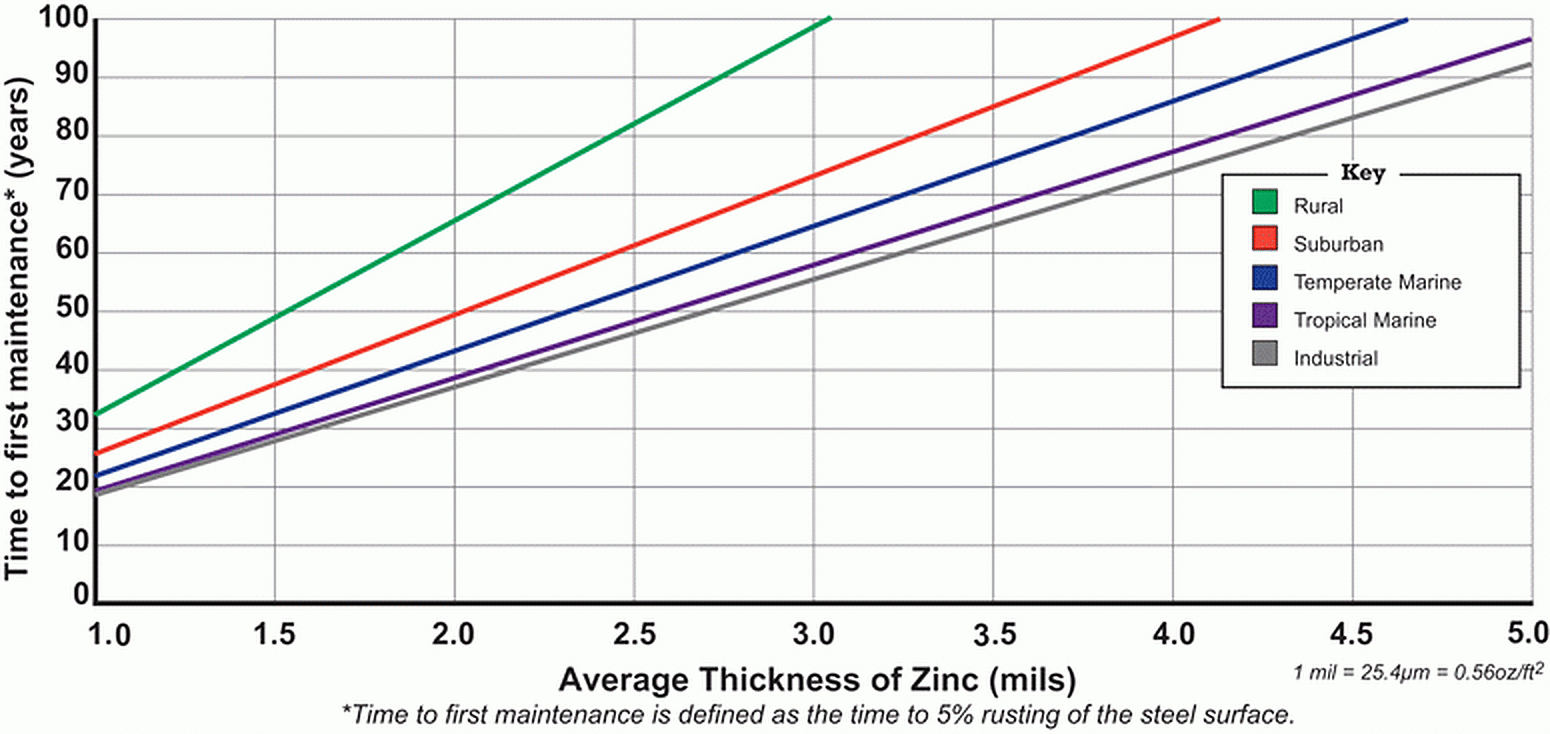
The corrosion rate of zinc is directly influenced by atmospheric conditions. Certain factors that specifically affect the corrosion of zinc include: temperature, humidity, rainfall, sulfur dioxide (pollution) concentration in the air, and air salinity. None of these factors can be singled out as the main contributor to zinc corrosion, but they all play a role in determining the corrosion protection hot-dip galvanized (zinc) coatings can provide in certain environments. When galvanizing is exposed to the natural wet and dry cycles of the atmosphere, it develops a series of zinc byproducts on the surface called the patina. The patina is stable and non-reactive unless exposed to aggressive chlorides or sulfides. The patina is a key component in the longevity of the hot-dip galvanized coating in the atmosphere. Independent and industry testing of galvanized steel samples over decades in industrial, urban, rural, and marine environments, with varying degrees of chlorides, sulfides and other corrosive elements, has yielded performance data for galvanized steel in real world applications. For results, view the Time to First Maintenance chart below.
© 2026 American Galvanizers Association. The material provided herein has been developed to provide accurate and authoritative information about after-fabrication hot-dip galvanized steel. This material provides general information only and is not intended as a substitute for competent professional examination and verification as to suitability and applicability. The information provided herein is not intended as a representation or warranty on the part of the AGA. Anyone making use of this information assumes all liability arising from such use.

