Design & Fabrication
As with all materials and coatings, there are certain practices which yield better quality finished products. In order to meet the expectations and demands of many different markets, it is important to understand and utilize the best design practices. These practices should be utilized once the decision to hot-dip galvanize has been made. Often no or only minor adjustments to the design are necessary, and worth the extra time and/or effort up front to alleviate potential future headaches based on design practices for other coating systems. Incorporating the design practices detailed here along with those listed in ASTM A385 Practice for Providing High Quality Zinc Coatings (Hot-Dip), will not only produce optimum quality galvanized coatings, but also help reduce costs and improve turnaround times.
Communication is Key
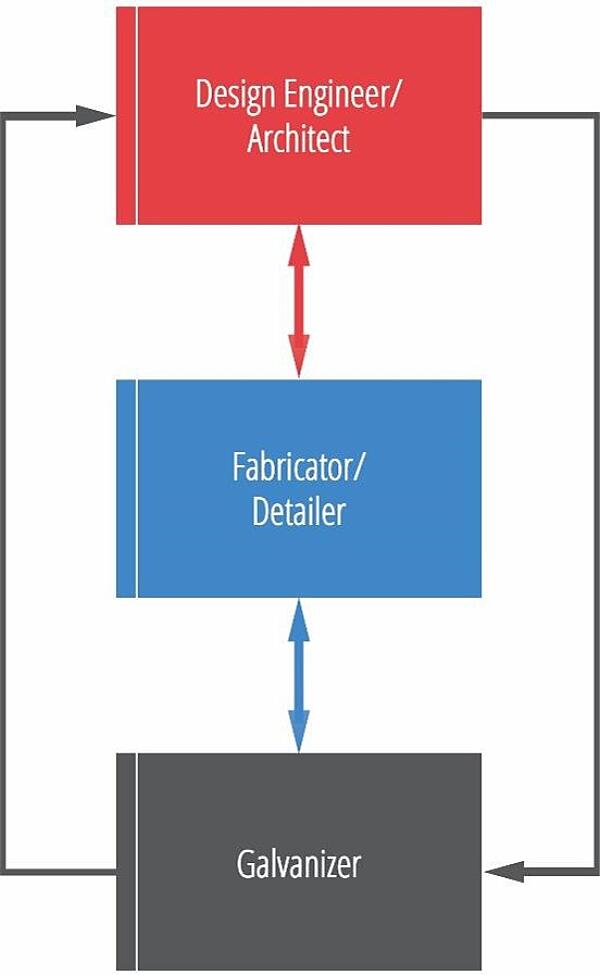
One key to providing the best design for the hot-dip galvanizing process is communication between the architect, engineer, fabricator and galvanizer. Opening the lines of communication early in the design process can eliminate potential costly pitfalls later in the process. A few good topics to cover while the project is being designed are:
- Steel Chemistry & Surface Condition
- Size & Shape
- Process Temperature/Heat
- Venting & Drainage
- Welding
- Threaded Parts/Connections
- Post-Galvanizing Deign/Use
Understanding these aspects of the galvanizing process and how they can affect the coating and finished products outcome will help ensure everyone's expectations are met.
Design Data Detail Software
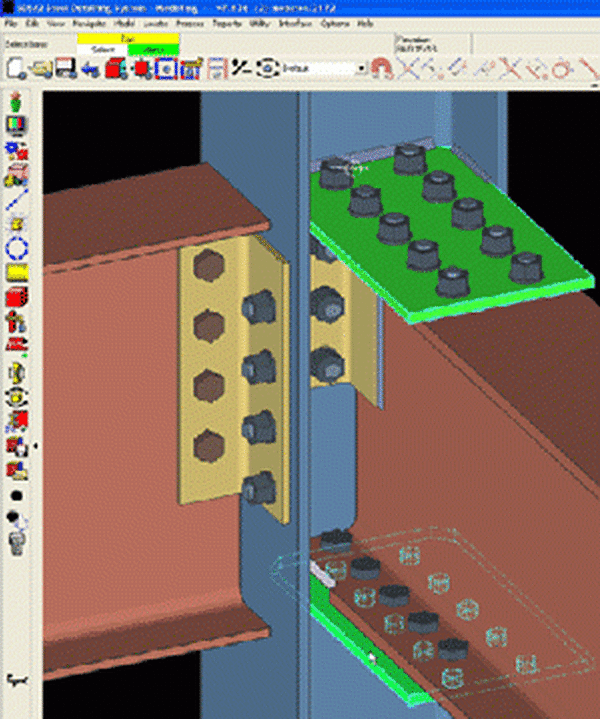
To aid in the communication process and ensure galvanizers receive steel fabricated with proper details, the AGA has been working with Design Data, a steel detailing software company. Design Data has now incorporated galvanizing details into their software program SDS/2. SDS/2 now allows the user to designate their fabriation will be hot-dip galvanized so the software can assist with proper design. The user can either designate hot-dip galvanizing at set up, as each member is designed, or after the design is complete. A few examples of what the software will facilitate when galvanizing is selected:
- Automated vent/drain locations and sizes
- Checks for kettle size fit, dissimilar materials, vents/drains, welds
- Defaults to American Institute of Construction (AISC) Standards