HDG & EPD
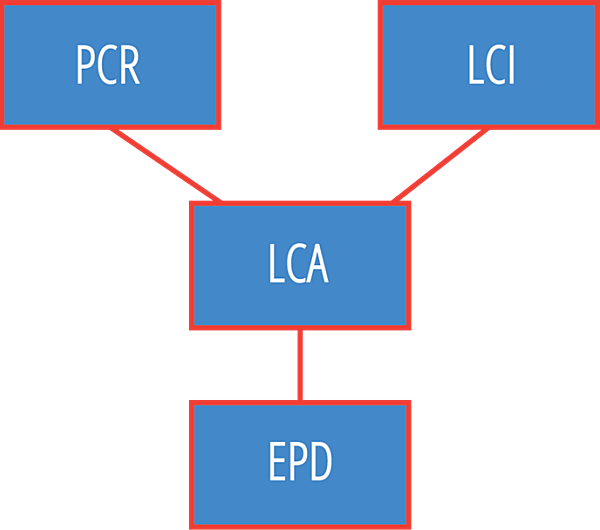
An Environmental Product Declaration (EPD) is a standardized way of quantifying the environmental impact of a product or system within a life-cycle assessment . Declarations include information on the environmental impact of raw material acquisition, energy use and efficiency, content of materials and chemical substances, emissions to air, soil, and water, and waste generation.
An EPD is created and verified in accordance with the International Standard ISO 14025, developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and are based on a LCA according to ISO 14040 and ISO 14044. In North America, the proliferation of EPDs was due to the new LEED® v4 requirements in the Materials & Resources credit category, which has a Building Product Disclosure and Optimization (BPDO) credit for EPDs.
While EPDs do educate consumers about the product and its environmental impact, consumers should know that it is for disclosure purposes only, and does not mean that the product meets any environmental performance standards. Furthermore, the BPDO credit within LEED® is achieved by selecting products with EPDs, but does not require the project team to select the most environmentally-friendly products.
In 2016, the AGA released an industry-wide Environmental Product Declaration (EPD) developed by world-renown environmental firm thinkstep, Inc. and verified by UL Environment, Inc. The background life-cycle assessment utilized galvanizing data collected from the AGA, zinc information collected from the International Zinc Association (IZA), and steel/fabrication information from the American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC), Steel Tube Institute (STI), and the GaBi database.

The EPD covers galvanized hot-rolled structural sections, plate, and hollow structural sections (HSS). In addition to the full EPD, the AGA released three transparency briefs one on each product type. The EPD and briefs were developed in accordance with ISO 14025 including background LCA in accordance with ISO 14040/14044 standards according to the product category rule (PCR) for North America Designated Steel Construction Products.
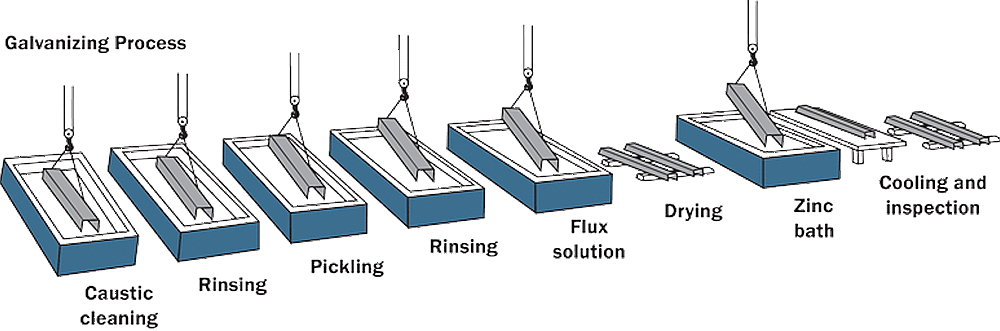
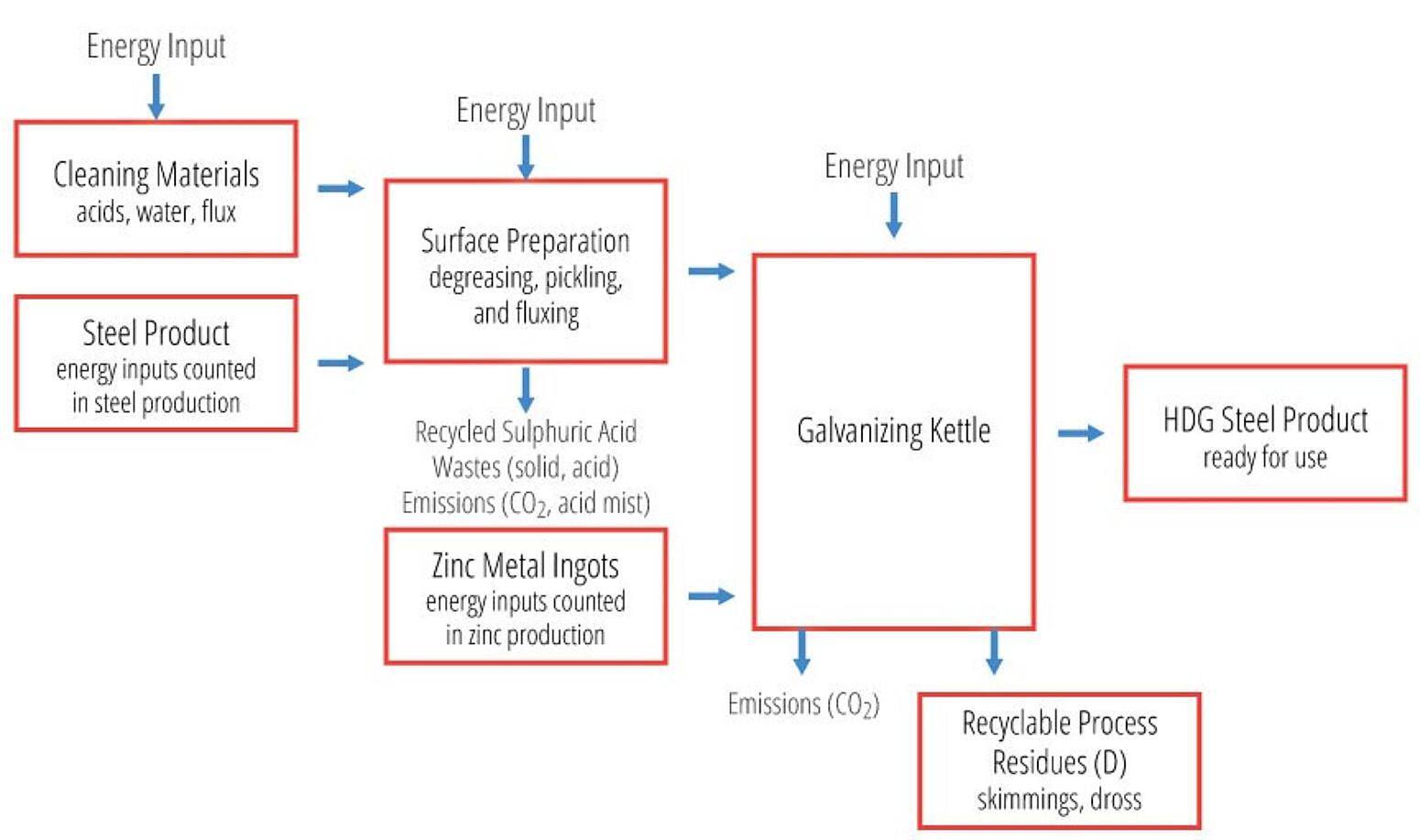
The EPD is a cradle-to-gate study representing the raw materials supply (A1), transport (A2), and manufacturing stages of hot-dip galvanized steel (A3), as well as the benefits associated with the recovery of zinc scrap during the galvanizing process (D). The raw material stage (A1) accounts for raw material acquisition of both the steel and the zinc, as well as steel making and fabrication and zinc concentration and refining.
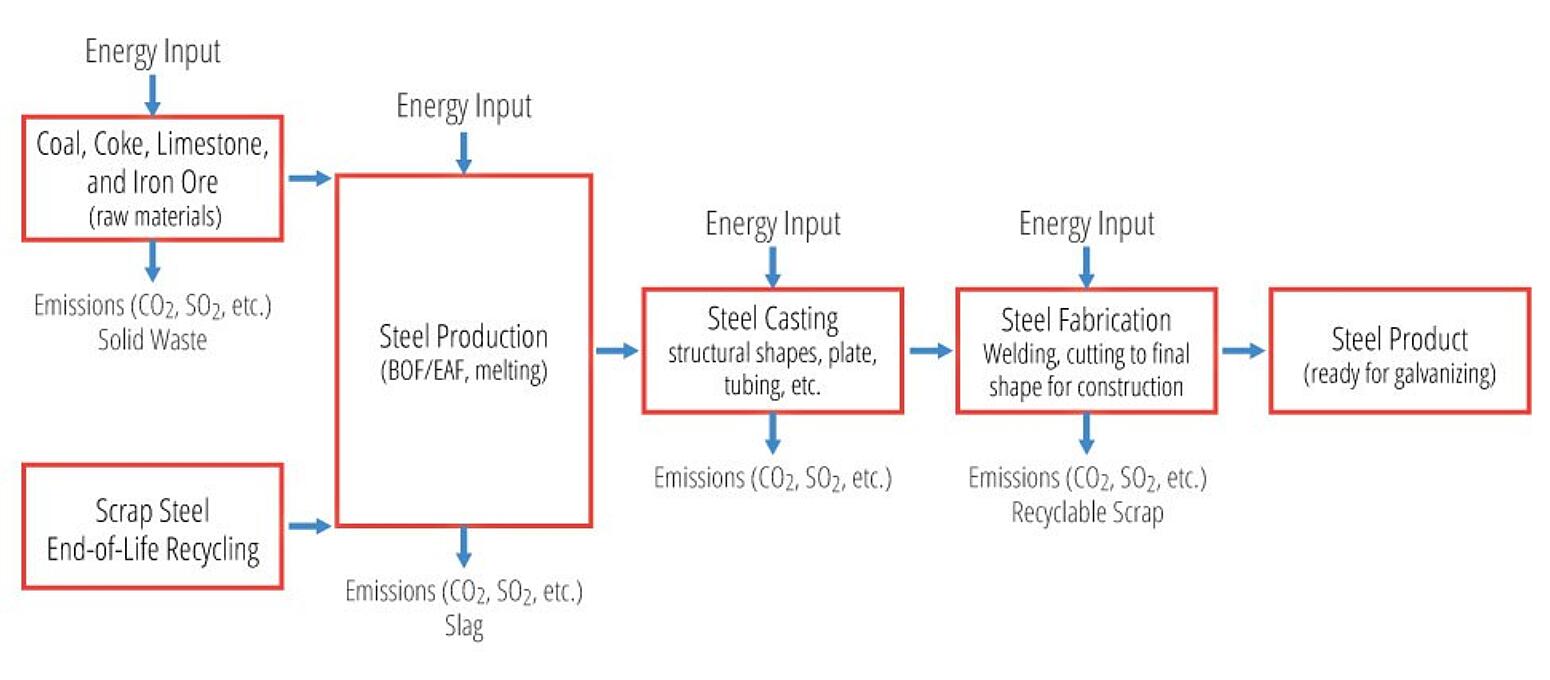
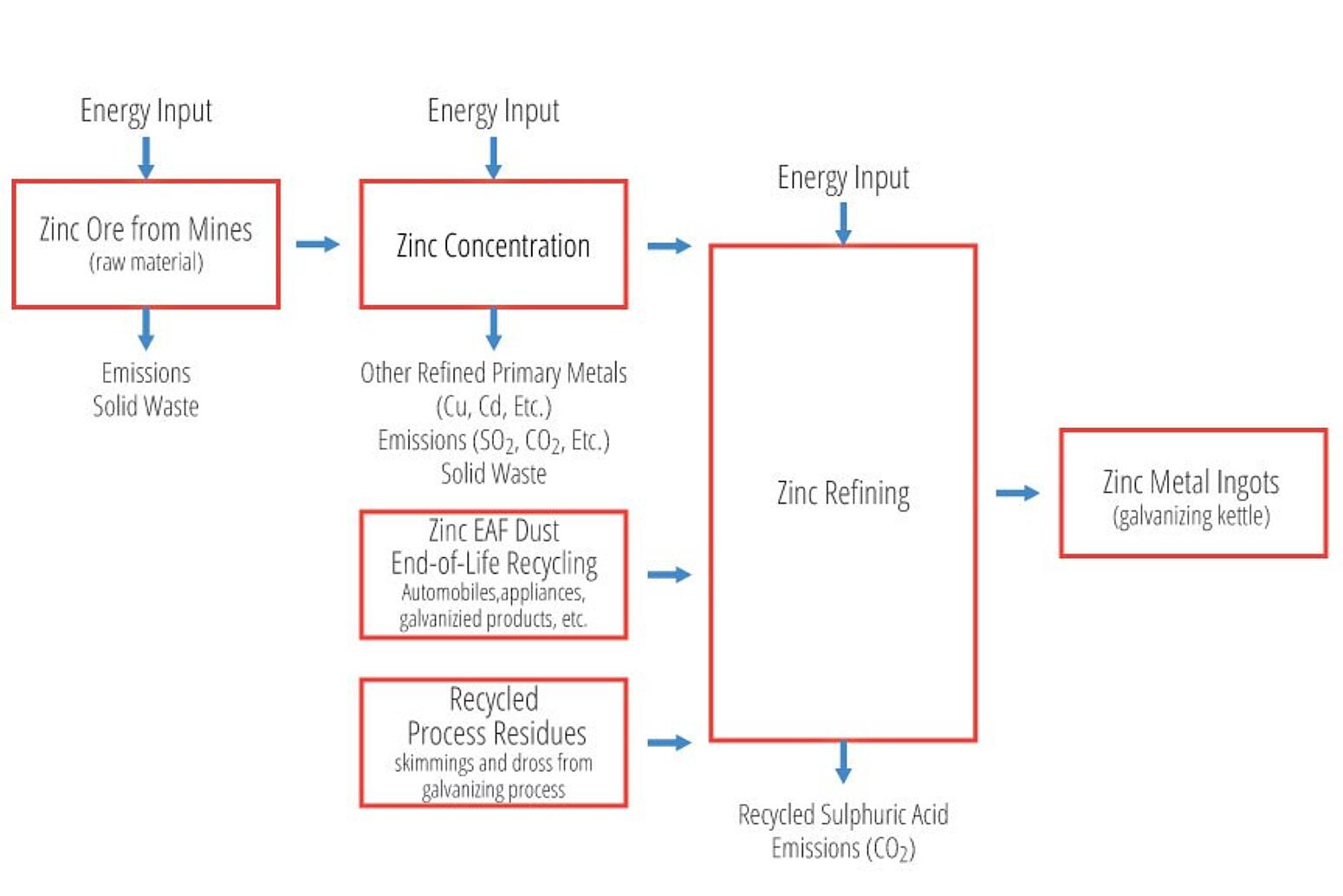
The manufacturing stage (A3) accounts for the application of the zinc metal to the steel through the hot-dip galvanizing process. The credit (D) only accounts for recycling during the production of the hot-dip galvanized coating (zinc dross and skimmings), and not for the full recyclability of the hot-dip galvanized steel product at the end of life.